Abstract.
The development of a laser photoelectron
projection microscope with a magnification up to $10^5$
and spatial resolution up to $30\; nm$ as well as the
first results of studies of needle tips made of $LiF$
crystals with $F_2$-aggregated centers with the use of
this microscope are reported. The resolution achieved was
sufficient to visualize individual defects on the
crystals surface. The effects of thermal faceting of
$LiF:F_2^-$ needle tips due to their heating by intense
laser radiation were observed for the first time.

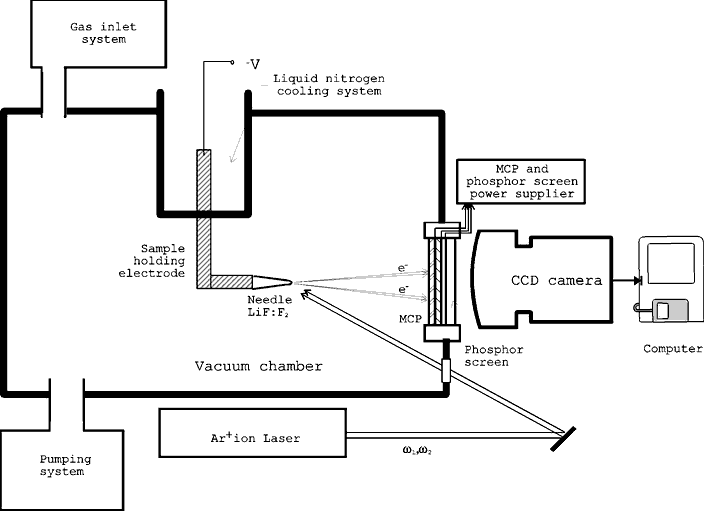
Fig.1 Scheme of the laser photoelectron projection microscope.
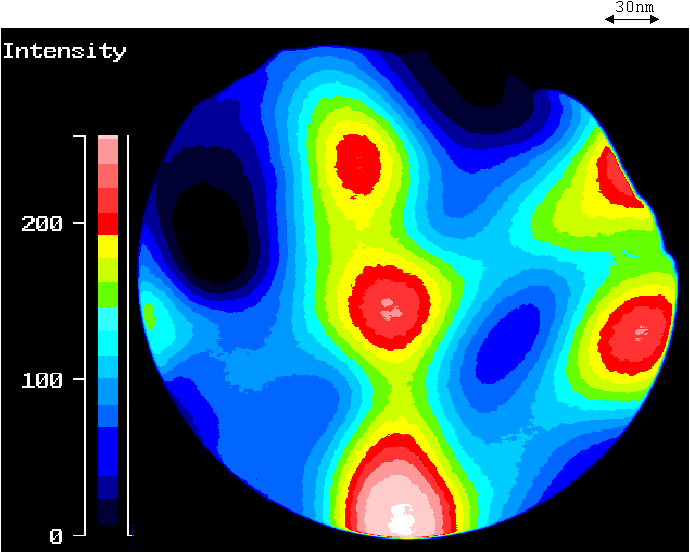
Fig.2 A photoelectron image of the $LiF:F_2$ needle tip with the concentration of $F_2$-centers $n\simeq 10^{16}\; cm^{-3}$. The radius of the needle tip $r\simeq 600\; nm$; the tip is irradiated by all the lines of $Ar^+$ laser with the intensity $I\simeq 5\cdot 10^3\; W/cm^2$.